Weekly Test I (2022-2023)
Physics
Class XII
SET-1
Date : 13.05.2022
Duration : 1 Hour 15 Minutes
No. of Pages : 6
M. Marks : 35
General Instructions
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) The question paper has four sections: Section A, Section B, Section C and Section D. There are 18 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
(iii) Section A has 8 questions of 1 mark each. Section B has 5 questions of 2 marks each. Section C has 4 questions of 3 marks each. Section D has a case-based question of 5 marks.
(iv) There is no overall choice in the paper.
Section A
1. An electric dipole has the magnitude of its charge as q and its dipole moment is p. It is placed in a uniform electric field E. If its dipole moment is along the direction of the field, the force on it and its potential energy are respectively : (1 Marks)
(a) 2qE and minimum
(b) qE and pE
(c) Zero and minimum
(d) qE and maximum
2. The electric charges are distributed in a small volume. The flux of the electric field through a surface of radius 10 cm surrounding the total charge is 20 Vm. The flux over a concentric sphere of radius 20 cm will be (1 Mark)
(a) 20 Vm
(b) 25 Vm
(c) 40 Vm
(d) 200 Vm
3. The SI unit of conductivity is (1 Mark)
(a) ohm
(b) mho
(c) ohm-m
(d) mho/m
4. An electric charge 10^-3 µC is placed at the origin (0,0) of x-y coordinate system. Two points A and B are situated at (√2, √2) and (2,0) respectively. The potential difference between the points A and B will be (1 Mark)
(a) 9 V
(b) Zero
(c) 4.5 V
(d) 2 V
5. The electrostatic potential on the surface of a charged conducting sphere is 100 V. Twi statements are made in this regard.
S1 : At any point inside the sphere, electric intensity is zero.
S2 : At any point inside the sphere, the electrostatic potential is 100 V.
Which of the following is a correct statement? (1 Mark)
(a) S1 is true but S2 is false.
(b) Both S1 and S2 are false.
(c) S1 is true, S2 is true and S1 is the cause of S2.
(d) S2 is true, S2 is also true but the statements are independent.
6. 6. Consider a uniform electric field in the z-direction. The following statements are made :
(i) The potential is a constant in all space.
(ii) The potential is constant for any x for a given z.
(iii) The potential is constant for any y for a given z.
(iv) The potential is constant on the x-y plane for a given z.
The correct statement(s) is(are) :
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Assertion – Reasoning Questions
Note : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
7. Assertion : For identical charges of magnitude q each are placed at the vertices of a square of side ‘a’. The electric field at the central point O is zero but electric potential is non-zero and finite.
Reason : Electric field is a vector quantity but electric potential is a scalar. (1 Mark)
8. Assertion : The whole charge of a conductor cannot be transferred to another conductor.
Reason : Total transfer of charge from one body to another is against the law of conservation of electric charge. (1 Mark)
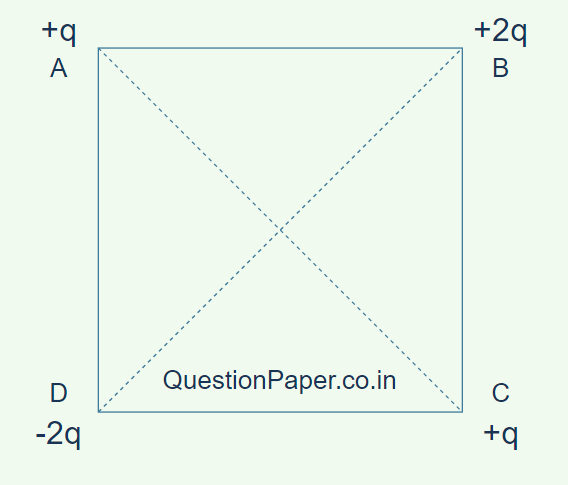
9. Four point charges are kept at the four vertices of a square of side 2L as shown in the figure below. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force on a charge of 1 µC placed at the centre of the square. (2 Marks)
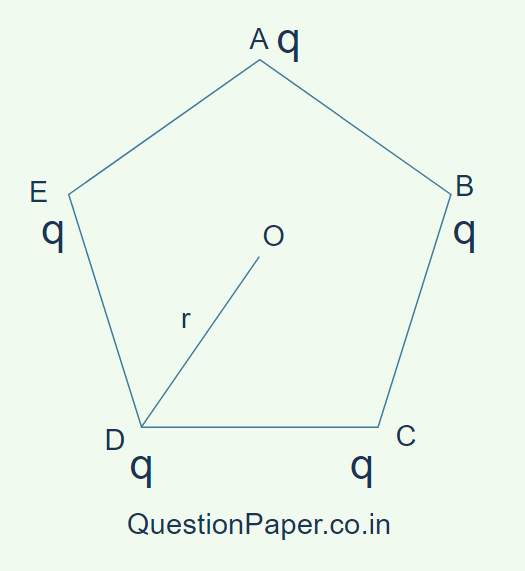
10. Five charges, each of magnitude ‘q’ are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon of side ‘a’ as shown in the figure below. (2 Marks)
(a) Compute the resultant electric field at O, the centre of the pentagon.
(b) How would your answer be affected if pentagon is replaced by n sides polygon with charge ‘q’ at each of its corners?
11. Two metallic spheres of radii R and 2R are charged so that both of these have the same surface charge density symbol σ. If they are connected to each other with a conducting wire, in which direction will charges flow and why? (2 Marks)
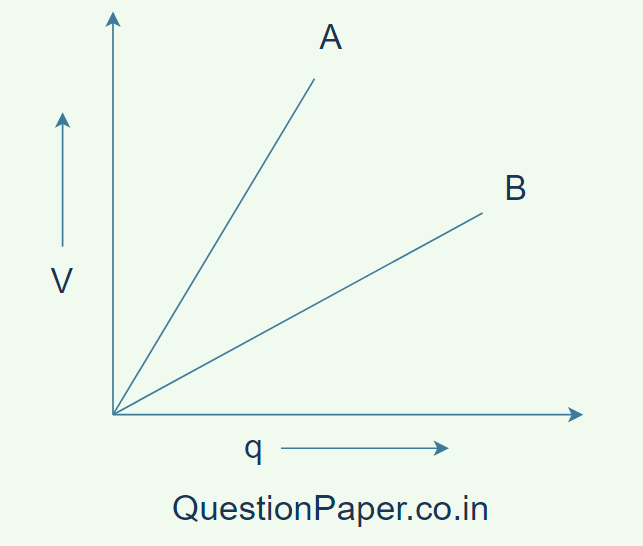
12. The given graph shows variation of charge ‘q’ with potential ‘V’ for two capacitors C1 and C2. Both the capacitors have same plate area but plate separation of C2 is double than that of C1.
(a) Which line (A or B) corresponds to C1?
(b) Which will store more energy? Justify your answer in each case.
13. State Ohm’s Law and express it mathematically. (2 Marks)
Section – C
14. Using Gauss’s theorem, prove that the electric field intensity due to an infinitely long thin straight charged wire at a point P at a distance ‘r’ from the wire is inversely proportional to ‘r’. (3 Marks)
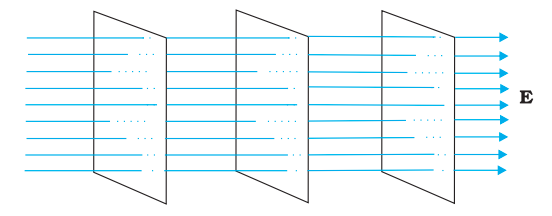
15. Equipotential surfaces are surfaces at which the potential is same at every point. Refer to the figures (A) and (B) shown below. Infer the type of electric field depicted in each case. Give reason for your answer in each case. (3 Marks)

16. (a) Write the equations for electrostatic potential energy of a system of two charges (i) in the absence of external electric field (ii) in the presence of external field. (3 Marks)
(b) A proton approaches another proton. What happens to :
(i) the kinetic energy of the approaching proton.
(ii) the electrostatic potential energy of the system.
17. A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is charged by a battery to a potential V.
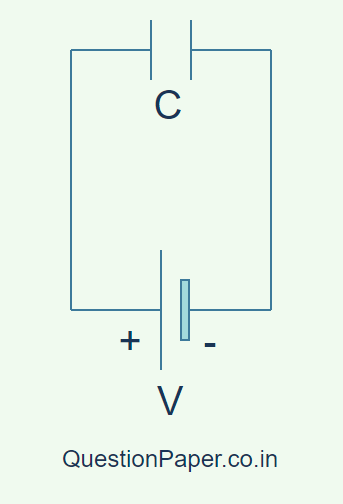
Without disconnecting the battery, the distance between the plates is tripled and a dielectric medium of K=10 is introduced between the plates.
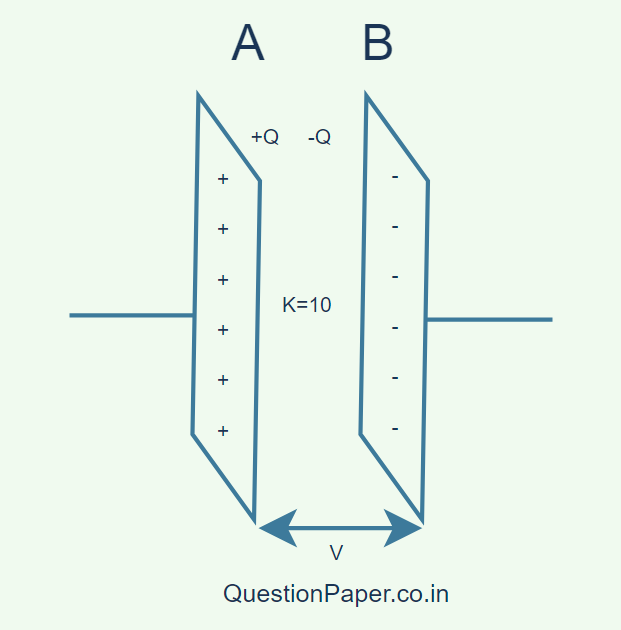
How will (i) the capacitance (ii) electric field between the plates, and (iii) the energy stored between the plates, be affected? Support your answer with suitable mathematical calculations.
Section – D
18. Static Charges [5 Marks]
When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, the rod acquires one kind of charge and the silk acquires the second kind of charge. This is true for any pair of objects that are rubbed to be electrified. Now if the electrified glass rod is bought in contact with silk, with which it was rubbed, they no longer attract each other. They also do not attract or repel other light objects as they did on being electrified.

Thus, the charges acquired after ribbing are lost when the charged bodies are brought in contact. By convention, the charge on glass rod or cat’s fur is called positive and that on plastic rod or silk is termed negative. If an object possesses an electric charge, it is said to be electrified or charged. When it has no charge it is said to be electrically neutral.
(i) On charging a neutral Balloon its size
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) remains same
(d) No relation between charge and size
(ii) Charge on a body is integral multiple of ±e. It is given by
(a) conservation of charge
(b) conservation of mass
(c) conservation of energy
(d) quantization of charge
(iii) Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B, of identical sizes and each of charge 6.5×10^-7 C have their centres separated by a distance of 50 cm. What is the force of repulsion between A and B?
(a) 1.25×10^-2 N
(b) 1.52×10^-2 N
(c) 2.25×10^-2 N
(d) 1.21×10^-2 N
(iv) In part (iii), suppose each sphere is charged double the amount and distance between them is halved, what is the new force of repulsion between A and B?
(a) 64×10^-2 N
(b) 35×10^-2 N
(c) 24×10^-2 N
(d) 50×10^-2 N
(v) In part (iii), suppose a third sphere of the same size but uncharged is brought in contact with the first, then brought in contact with the second, and finally removed from both. What is the new force of repulsion between A and B?
(a) 5.2×10^-3 N
(b) 5.7×10^-3 N
(c) 6.2×10^-3 N
(d) 1.2×10^-3 N